Mastering PDF Accessibility Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding PDF Accessibility and Why It Matters
Did you know that inaccessible PDFs can shut out millions of users with disabilities? Ensuring PDF accessibility isn't just a compliance issue; it's about providing equal access to information for everyone. Let's dive into why PDF accessibility matters and how to achieve it.
PDF accessibility means designing PDFs so that people with disabilities can use them effectively. This involves making the content perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust, aligning with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). Accessible PDFs enable users with disabilities to access content using assistive technologies like screen readers.
- Usability for all: Accessible PDFs ensure that individuals with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive disabilities can access and understand the information.
- Compliance with standards: Adhering to standards such as wcag, PDF/UA, and Section 508 is crucial for legal compliance and ensuring broad accessibility. Section508.gov offers resources for understanding and meeting these standards.
- PDF processing tools: Specialized tools are vital for creating, testing, and remediating PDFs to meet accessibility requirements. These tools are essential for the testing and remediation processes we will explore next. They automate complex tasks, ensure consistency, and are often the only way to perform certain accessibility remediations.
Creating accessible PDFs is essential for legal, ethical, and business reasons. It ensures inclusivity and compliance, while also expanding your audience.
- Legal requirements: Non-accessible PDFs can lead to discrimination lawsuits. Compliance with laws like Section 508 in the U.S. is crucial.
- Ethical considerations: Providing equal access to information is a fundamental ethical responsibility. Everyone deserves the same opportunity to access and understand content.
- Business benefits: Accessible PDFs reach a wider audience, improving brand reputation and customer satisfaction. By making content accessible, businesses can tap into a broader market.
Many PDFs contain accessibility barriers that prevent users with disabilities from accessing the information. Identifying and addressing these issues is the first step toward creating accessible documents.
- Lack of proper tagging: Without correct tags, screen readers can't interpret the content accurately.
- Missing alternative text: Images without alt text are inaccessible to visually impaired users.
- Poor color contrast: Low contrast ratios make it difficult for users with low vision to read the text.
- Improper reading order: Incorrect reading order can confuse screen reader users, presenting content in an illogical sequence.
- Untagged forms: Inaccessible form fields make it impossible for users with assistive technologies to complete and submit forms.
Understanding these issues is the first step in creating accessible PDFs. Next, we'll explore the tools and techniques for testing PDF accessibility to ensure compliance and inclusivity.
Automated PDF Accessibility Testing
Ever wondered if a robot could check your PDFs for accessibility? Automated testing is here to help! It offers a fast and consistent way to identify common accessibility issues, though it's not a complete solution.
Automated accessibility checkers are software tools designed to scan PDFs for compliance with accessibility standards. Popular options include Adobe Acrobat Pro and PAC (PDF Accessibility Checker). These tools systematically analyze various aspects of a PDF, such as tagging, alternative text, color contrast, and document structure.
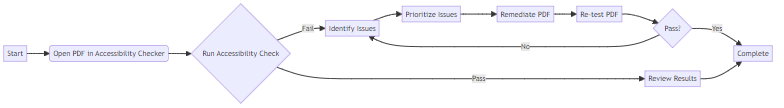
Running an accessibility check typically involves opening the PDF in the chosen tool and initiating the accessibility check feature. For instance, in Adobe Acrobat Pro, you would go to "All tools > Prepare for accessibility > Check for accessibility." The tool then generates a report detailing any identified issues, categorized by severity and type.
Interpreting the results is crucial for effective remediation. Accessibility checkers usually provide a pass/fail status for each tested element. Understanding the specific issues flagged, such as "missing alternative text" or "insufficient color contrast," allows you to target remediation efforts efficiently.
One of the most significant advantages of automated testing is its efficiency. As Deque Systems, Inc. notes, automated scans can monitor the breadth and depth of your sites. This allows organizations to test a large number of documents quickly, saving considerable time and resources compared to manual testing.
Automated testing also ensures consistency by applying the same rules and criteria to all documents. This eliminates subjective interpretations and ensures that all PDFs are evaluated against the same standards. However, automated tools have limitations. They cannot assess contextual issues or complex relationships within the content, which often require human review. For example, an automated tool might not understand the intended meaning of a specific image or the logical flow of a complex, multi-part table.
According to Deque Systems, Inc., "80% of your testing effort should be automated and 20% should be manual."
Several key accessibility checks can be effectively automated. Tagged PDF verification ensures that the document has a proper logical structure, which is essential for screen readers to interpret the content correctly. Alternative text checks identify missing or inadequate alt text for images, which is crucial for users with visual impairments.
Color contrast analysis detects instances where the contrast between text and background colors is insufficient, making it difficult for users with low vision to read the text. Finally, checking the document language setting ensures that the language is correctly identified, allowing screen readers to use the appropriate pronunciation and grammar rules.
While automated testing offers numerous benefits, it's important to remember that it is just one part of a comprehensive accessibility testing strategy. Next, we'll explore manual PDF accessibility testing techniques.
Manual PDF Accessibility Testing
Manual PDF accessibility testing is like putting on the glasses of a user with disabilities to see the document as they would. While automated tools catch many issues, they often miss the nuances that affect real-world usability.
Addressing limitations of automated testing: Automated tools can't understand context or meaning. Manual testing allows you to evaluate whether the purpose of the content is clear, which machines can't determine.
Testing with assistive technologies: Simulating the experience of users with disabilities is crucial. Testing with screen readers, for example, reveals issues like incorrect reading order or missing alternative text that automated tests might overlook.
Verifying reading order: Ensuring a logical content flow is essential for screen reader users. Manual testing confirms that the reading order makes sense and follows a coherent path through the document.
Keyboard navigation: Test if all interactive elements are reachable and operable using only the keyboard. This ensures accessibility for users who cannot use a mouse.
Screen reader testing: Use tools like NVDA, JAWS, or VoiceOver to navigate the PDF. Listen to how the content is presented and identify any missing or confusing information.
Visual inspection: Check for sufficient color contrast, appropriate font sizes, and a clear layout. Poor visual design can create barriers for users with low vision.
No sound testing: Verify that all audio elements have appropriate alternatives, such as captions or transcripts. This is vital for users who are deaf or hard of hearing.
Complex tables: Ensure that tables are structured correctly with proper headers and summaries. Screen readers need this information to convey the table's content effectively.
Forms: Verify that form fields have clear labels, instructions, and validation messages. Assistive technology users should be able to easily understand and complete forms.
Multimedia: Check that videos have captions, transcripts, and audio descriptions. This makes multimedia content accessible to users with hearing or visual impairments.
Links: Confirm that link text accurately describes the destination and purpose of the link. Avoid generic text like "click here," which provides no context.
Manual testing requires a human touch to uncover accessibility issues that automated tools can't detect. By using these techniques, you can ensure your PDFs are truly accessible to everyone.
Let's move on to understanding how real users interact with your documents.
User Testing with People with Disabilities
Is your PDF truly accessible if it hasn't been tested by the people who will use it most? User testing with people with disabilities provides invaluable insights that automated and manual tests simply can't capture. Here’s how to make it happen.
Real-world insights: Engaging users with disabilities offers a direct understanding of their experiences. By observing how they interact with your PDF, you gain firsthand knowledge of the barriers they encounter. This feedback is crucial for identifying issues that might be missed by automated tools or internal testing.
Identifying usability issues: User testing uncovers practical problems. For example, a visually impaired user might struggle with a complex table despite it having proper tags. This highlights the need for simplification or alternative presentation methods.
Improving accessibility: Iterative improvements based on user feedback lead to more accessible PDFs. Each round of testing and remediation brings the document closer to full accessibility, ensuring a better experience for all users. The number of rounds needed varies greatly depending on the complexity of the PDF and the severity of the issues found. Typically, a few rounds are sufficient, but it's an ongoing process driven by feedback until the users report a satisfactory experience.
Recruiting participants: Finding a diverse group of users is key. Include individuals with various disabilities (visual, auditory, motor, cognitive) and different levels of tech proficiency. Including participants with varying tech proficiencies is important because it helps understand how different levels of familiarity with assistive technologies might impact their experience and feedback.
Developing test scenarios: Create realistic tasks that users would typically perform with the PDF. For example, having them fill out a form, navigate to a specific section, or extract information from a chart.
Providing assistive technologies: Ensure users can use their preferred assistive technologies. Whether it's a specific screen reader, keyboard navigation setup, or voice recognition software, familiarity is key.
Gathering feedback: Observe users as they interact with the PDF. Ask clarifying questions and encourage them to voice their thoughts and frustrations. Document their experiences, noting both successes and challenges.
Prioritizing issues: Address the most critical problems first. Focus on issues that significantly impact usability and accessibility for the majority of users.
Making changes: Implement fixes based on user feedback. This might involve restructuring content, adding alternative text, improving color contrast, or simplifying navigation.
Retesting: After implementing changes, retest the PDF with users. This verifies that the fixes have indeed improved accessibility and identifies any new issues that may have arisen.
Incorporating user feedback ensures that your PDFs are not just technically compliant, but also genuinely usable for people with disabilities. Now, let's look at how to put all this into practice.
Practical Steps for PDF Accessibility Testing
Accessibility testing can feel daunting, but breaking it down into manageable steps makes the process much smoother. By creating a clear plan and following a structured process, you can ensure your PDFs meet accessibility standards.
A well-defined testing plan is the foundation of effective PDF accessibility testing. It ensures that all critical aspects are considered and that the testing process is systematic and thorough.
- Defining scope: Start by identifying which PDFs need testing. Prioritize those that are most frequently used or contain essential information. For instance, a healthcare provider might prioritize patient information forms, while a retail company focuses on product catalogs and user manuals.
- Setting goals: Determine the desired level of accessibility. Are you aiming for basic compliance, or striving for a highly usable experience for all users? Knowing this helps tailor the testing effort.
- Choosing methodologies: Decide which testing methods to use, such as automated checks, manual reviews, and user testing. Combining these approaches provides a comprehensive view of accessibility.
- Assigning roles: Delegate responsibilities to team members. Assign specific tasks based on their skills and expertise. Common roles include:
- Accessibility Tester: Responsible for conducting automated and manual checks, identifying issues, and documenting findings.
- Content Creator/Editor: Responsible for creating and updating content, ensuring it's structured accessibly from the start, and implementing remediation based on test reports.
- Remediation Specialist: Focuses specifically on fixing identified accessibility issues within the PDF.
- Project Manager: Oversees the entire accessibility testing process, ensuring timelines are met and resources are allocated effectively.
A structured testing process ensures consistency and thoroughness. Each step builds upon the previous one, leading to a comprehensive assessment of PDF accessibility.
- Automated testing: Run automated accessibility checkers like Adobe Acrobat Pro, as mentioned earlier, and carefully review the results. These tools can quickly identify common issues, such as missing alternative text or incorrect tagging.
- Manual testing: Perform manual checks, including keyboard navigation, screen reader testing, and visual inspection. This is crucial for uncovering issues that automated tools might miss.
- User testing: Recruit participants with disabilities to test the PDF. Gather their feedback on usability and accessibility, which provides invaluable insights. As explored earlier, user feedback ensures that your PDFs are genuinely usable for everyone.
- Reporting: Document all accessibility issues and recommendations. Provide clear and actionable feedback to the remediation team.
Having the right tools and resources is essential for effective PDF accessibility testing. These tools help streamline the testing process and ensure accurate results.
- Accessibility checkers: Use tools like Adobe Acrobat Pro to automate many tasks, check accessibility, and provide instructions for manual fixes, as mentioned earlier.
- Screen readers: Employ screen readers like NVDA, JAWS, or VoiceOver to experience the PDF as a visually impaired user would.
- Color contrast analyzers: Utilize tools like the WebAIM Contrast Checker to ensure sufficient color contrast between text and background.
- Web accessibility guidelines: Refer to wcag and PDF/UA for detailed standards and best practices.
By following these practical steps, you can create and implement a robust PDF accessibility testing process. Now, let's talk about making accessibility a regular part of your work.
Integrating Accessibility Testing into Your Workflow
Integrating accessibility testing into your workflow isn't just a step; it's a commitment to inclusivity that should be woven into the fabric of your processes. But how do you make accessibility a seamless part of your everyday work?
Creating accessible source documents is the first step. By using accessible templates and styles in programs like Microsoft Word or Google Docs, you lay a solid foundation. To find or create these, look for built-in templates that emphasize structure (e.g., heading styles, list styles). If you're creating your own, ensure you consistently use heading styles for document structure, apply list formatting correctly, and use the software's accessibility checker before converting to PDF. Resources like Microsoft's accessibility documentation or guides from accessibility organizations can offer specific advice. This ensures that headings, lists, and other structural elements are properly tagged from the outset, making the PDF conversion process smoother.
It's also vital to train content creators on accessibility best practices. Educating staff about the importance of alt text, sufficient color contrast, and proper heading structures can significantly reduce accessibility issues down the line.
Finally, selecting accessible PDF creation tools is crucial. Choose software that supports accessibility features, allowing for proper tagging and metadata to be embedded during PDF generation. Look for tools that offer options for setting document language, creating tagged PDFs, and exporting with accessibility tags intact.
Early testing is key to identifying accessibility issues early in the process. Running automated checks on draft PDFs helps catch common errors like missing alt text or insufficient color contrast before they become ingrained.
Iterative testing involves making ongoing improvements based on feedback. After each round of testing whether automated, manual, or user-based implement the necessary changes and re-test to ensure the fixes are effective.
Before publishing, conduct a final review to ensure all accessibility standards are met. This includes both automated checks and manual testing.
Regular audits are essential for ensuring continued accessibility. Periodically retesting PDFs, especially after updates or modifications, helps identify any new issues that may have arisen. For example, adding new images, tables, or text sections to an existing PDF might introduce new accessibility barriers that require a review.
Updating content should always include an accessibility review. Ensure that any new content added to existing PDFs adheres to accessibility guidelines.
Finally, staying informed about the latest accessibility standards and best practices is vital. Accessibility is an evolving field, and keeping up-to-date ensures your PDFs remain compliant and usable for everyone.
By integrating these practices into your workflow, you can create PDFs that are accessible, inclusive, and compliant with accessibility standards. Let's look at a tool that can help streamline this.
Leveraging PDF7 for Streamlined Document Processing and Enhanced Accessibility
Streamlining PDF management and enhancing accessibility doesn't have to be a headache. PDF7 emerges as a versatile solution, designed to simplify document processing and ensure inclusivity for all users. PDF7 is a software application (or suite of tools) that helps users manage and edit PDF files.
Effortlessly merge, rotate, and organize PDFs with PDF7's intuitive interface, saving valuable time and resources. Imagine a retail company consolidating multiple product catalogs into a single, easily navigable PDF for customers.
Remove unnecessary pages and extract essential information, optimizing your documents for clarity and accessibility. Think of a healthcare provider streamlining patient records by removing redundant pages, focusing on critical medical history.
Seamlessly convert various file formats to PDF, ensuring consistency and compatibility across different platforms. Consider a financial institution converting diverse documents (Word, Excel, images) into a unified PDF format for secure archiving.
Convert PDFs to accessible formats like Word, allowing for easy editing and remediation to meet accessibility standards. This enables quick fixes to meet wcag guidelines. Converting to Word allows for easier manipulation of tags, headings, and alt text compared to directly editing a PDF. You can then re-apply accessibility features within Word before converting back to an accessible PDF.
Utilize the text extender and paraphrasing tool to re-write the document in a simple way so everyone can understand the context. This tool, found within PDF7, helps simplify complex language. For example, if a document contains a sentence like "The synergistic interplay of disparate stakeholders necessitates a paradigm shift in operational efficacy," the paraphrasing tool might rephrase it to "When different groups work together, we need to change how we do things to be more effective."
Leverage PDF7's compression capabilities to reduce file size without compromising readability, making documents easier to share and access for users with limited bandwidth.
Secure sensitive information by protecting PDFs with passwords, ensuring only authorized users can access the content. This is vital for legal documents or confidential business reports.
Easily unlock PDFs to enable editing and accessibility enhancements, promoting collaboration and inclusivity.
Repair corrupted PDFs with PDF7's advanced repair functionality, ensuring your documents remain accessible and usable for all users.
By leveraging PDF7's features, organizations can create, manage, and share PDFs more efficiently, ensuring accessibility for everyone.