Mastering Lossless PDF Compression: Techniques and Tools
Understanding PDF Compression Fundamentals
Did you know that inefficient PDF compression can lead to slower workflows and bloated storage costs? Let's dive into the fundamentals of lossless PDF compression and how it can revolutionize document management.
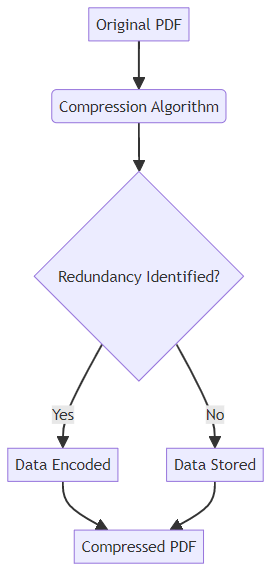
Lossless PDF compression reduces file size without sacrificing data integrity. This means every bit of information from the original PDF is preserved, ensuring perfect reconstruction upon decompression. It's crucial in industries where data accuracy is paramount.
- Key Benefit: Maintains original quality while reducing file size.
- Ideal for: Archiving, compliance, and long-term document storage.
- Examples: Legal documents, medical records, and financial statements.
Lossless compression algorithms identify and eliminate redundancy in the data. These algorithms include techniques like:
- Run-Length Encoding (RLE): Simplifies repetitive sequences of data.
- Huffman Coding: Assigns shorter codes to more frequent data elements.
- Deflate: A combination of LZ77 and Huffman coding. LZ77 is the algorithm that identifies redundancy by finding repeated sequences, and Huffman coding then further compresses the resulting data by assigning shorter codes to more frequent symbols.
Consider a healthcare provider needing to archive patient records. Using lossless compression ensures that every detail, from lab results to doctor's notes, remains intact while optimizing storage space. Similarly, financial institutions can use lossless compression for statements and reports, meeting regulatory requirements without increasing storage costs. Educational institutions can similarly use lossless compression for research compendiums, as the NHCE MCA Compendium of R&D Projects, a collection of research findings, demonstrates, efficient data management is crucial for digital documents.
Having understood these foundational algorithms, we can now delve into specific, powerful techniques like JBIG2, which excels at optimizing bi-level images.
JBIG2 Compression: Optimizing Bi-Level Images
Did you know that some PDF files, especially those with scanned documents, can be drastically reduced in size using a specialized compression technique? Let’s explore JBIG2 compression and how it optimizes bi-level images in PDFs.
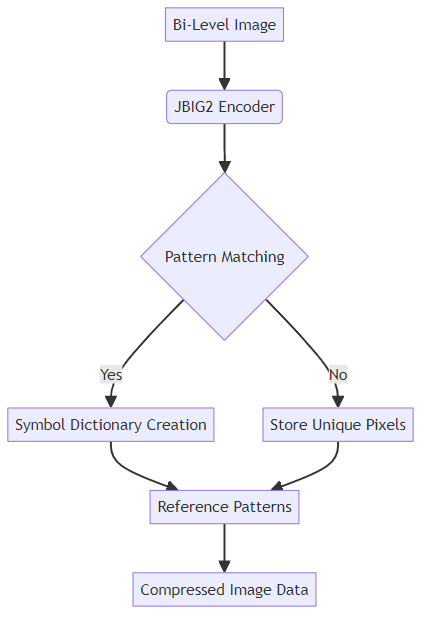
JBIG2 is a lossless compression standard particularly effective for bi-level images, meaning images with only two colors (typically black and white). This makes it ideal for scanned documents, faxes, and similar content. Unlike other compression methods that might blur or distort such images, JBIG2 preserves the crispness and clarity of the original.
- Superior Compression Ratios: JBIG2 often achieves significantly better compression than older methods like Group 4 fax compression, especially for text-heavy documents. This means smaller file sizes without sacrificing readability.
- Lossless Quality: As a lossless technique, JBIG2 ensures that every detail in the original image is perfectly preserved. This is vital for archiving and compliance purposes, where data integrity is non-negotiable.
- Optimized for Text: JBIG2 employs advanced pattern matching and substitution techniques specifically designed for text. This allows it to identify and efficiently compress repeated characters and words.
JBIG2 uses several sophisticated techniques to achieve its impressive compression rates. These include:
- Pattern Matching: Identifies recurring shapes and patterns (like characters in a text) within the image.
- Symbol Dictionary: Creates a dictionary of these common patterns.
- Substitution: Replaces each instance of a pattern with a reference to its entry in the dictionary.
Imagine a law firm archiving thousands of scanned legal documents. By using JBIG2 compression, they can significantly reduce storage costs while maintaining the legibility of every page.
While JBIG2 is excellent for bi-level images, it's not the best choice for color photographs or continuous-tone images. In those cases, other compression methods are more appropriate.
Now that we've explored JBIG2, let's move on to another important lossless compression technique: FlateDecode, which is particularly effective for compressing text and data streams within PDFs.
FlateDecode: Compressing Text and Data Streams
Did you know that much of the text you see in a PDF is compressed using a method that's been around for decades? Let's explore FlateDecode, a powerful lossless compression technique used extensively in PDF files to efficiently handle text and other data streams.
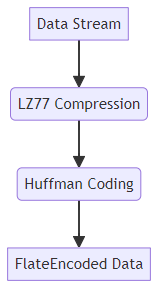
FlateDecode is a filter in PDF files that uses the zlib compression algorithm, which is based on the DEFLATE algorithm. This algorithm combines LZ77 (a lossless data compression algorithm) with Huffman coding to achieve effective compression. It's a workhorse for reducing the size of text, images, and other data embedded within a PDF, ensuring that files remain manageable without losing any information.
- Lossless Compression: Guarantees that the original data can be perfectly reconstructed upon decompression.
- Wide Applicability: Used for compressing various types of data streams within a PDF, including text, raster images, and metadata.
- Ubiquitous Support: Virtually all PDF readers and processors support FlateDecode, making it a reliable choice for compression.
FlateDecode operates in two main stages:
- LZ77 Compression: Identifies and replaces repeated sequences of data with references to earlier occurrences. This is particularly effective for text, where words and phrases are often repeated.
- Huffman Coding: Assigns shorter codes to more frequent symbols (bytes) and longer codes to less frequent ones. This further reduces the size of the data.
FlateDecode’s versatility makes it indispensable across various industries.
- E-commerce: Online retailers can use FlateDecode to compress product catalogs and user manuals, reducing bandwidth consumption and improving download speeds for customers.
- Financial Services: Banks and insurance companies rely on FlateDecode to compress account statements, policy documents, and regulatory filings, ensuring efficient storage and transmission of sensitive data.
- Education: Universities and online learning platforms use FlateDecode to compress lecture notes, research papers, and e-books, making them easier to distribute and access for students.
As we've seen, FlateDecode is a versatile tool for lossless compression within PDFs. Next, we'll explore object stream compression, another technique that enhances PDF efficiency.
Object Stream Compression
Ever wondered how PDFs handle large amounts of data efficiently? The answer lies, in part, with object stream compression, a technique that bundles multiple small objects into a single stream for better compression.
Object stream compression is a method used in PDFs to group smaller objects, such as text snippets or metadata, into a single stream. This stream is then compressed using algorithms like FlateDecode (as discussed earlier), leading to more efficient compression ratios. By reducing the overhead associated with individual objects, object streams contribute to smaller file sizes and faster processing.
- Reduced Overhead: Combining multiple objects into a single stream minimizes the overhead associated with individual object headers and metadata.
- Improved Compression: Applying compression algorithms to a larger stream of data often results in better compression ratios compared to compressing each object separately.
- Efficient Resource Usage: Object streams optimize the use of resources by reducing the number of individual objects that need to be managed.
Object streams work by first identifying suitable small objects within the PDF. These objects are then combined into a single stream, which is compressed using a standard compression algorithm. The PDF structure is updated to reference the compressed stream, allowing PDF readers to efficiently decompress and access the objects as needed. As the NHCE MCA Compendium of R&D Projects highlights, efficient data management is crucial for digital documents.
Object stream compression is particularly useful in scenarios where a PDF contains numerous small objects.
- E-books: Digital books with many short paragraphs or annotations can benefit from object stream compression.
- Technical Manuals: Complex manuals with numerous small diagrams and labels can be efficiently compressed using this technique.
- Archived Documents: Large collections of scanned documents, such as those used in research compendiums as noted earlier, often contain numerous small text fragments that can be compressed using object streams.
As we've explored object stream compression, let's now turn our attention to font subsetting and compression, another essential technique for optimizing PDF file sizes.
Font Subsetting and Compression
Did you know that the fonts embedded in a PDF can significantly impact its file size? Font subsetting and compression are key techniques to minimize this impact while ensuring the document remains legible.
Font subsetting involves including only the specific characters (glyphs) used in a document, rather than the entire font file. This is particularly useful for documents that only use a small portion of a font's character set. By discarding unused glyphs, the size of the embedded font is drastically reduced.
- Reduced File Size: Subsetting can significantly decrease the PDF file size, especially when using large or complex fonts.
- Improved Performance: Smaller font files translate to faster loading and rendering times, enhancing the user experience.
- Compliance: Ensures that only the necessary font data is included, which can be important for certain compliance requirements.
In addition to subsetting, fonts are often compressed using lossless algorithms to further reduce their size. Common compression methods include FlateDecode, which we discussed earlier. Once the font is subsetted, the resulting data stream is then passed through a lossless compression algorithm like FlateDecode, further reducing its size by identifying and encoding repeating patterns within the character data.
Font subsetting and compression are essential for various industries:
- Publishing: E-book publishers can use these techniques to reduce the file size of their publications, making them easier to download and distribute.
- Marketing: Marketing agencies creating visually rich brochures and reports can optimize PDFs for online sharing, ensuring fast loading times for potential clients.
- Legal: Law firms dealing with large volumes of legal documents can benefit from smaller, more manageable files, as the NHCE MCA Compendium of R&D Projects has shown the importance of data management in digital documents.
By carefully managing fonts, organizations can ensure their PDFs are both visually appealing and efficiently sized.
Now that we've covered font subsetting and compression, let's explore advanced techniques and considerations for lossless PDF compression.
Advanced Techniques and Considerations
Did you know that even with lossless compression, there's still room for optimization? Let's explore some advanced techniques and important considerations to squeeze every last bit of efficiency out of your PDFs.
The order in which you apply different compression techniques can impact the final file size. For example, applying FlateDecode to object streams after other optimizations may yield better results. This is because applying a general compression like FlateDecode to already optimized object streams might be less effective than applying it to the raw data before object stream creation, or vice-versa, depending on the specific algorithms and data. Experimentation and testing are key to finding the optimal workflow for your specific types of documents.
- Content Analysis: Before compressing, analyze the content of your PDFs. Are they primarily text-based, image-heavy, or a mix? This informs which techniques will be most effective.
- Iterative Compression: Some tools allow for multiple passes of compression. This can be beneficial, as each pass identifies and removes additional redundancy.
- Testing: Always test your compressed PDFs to ensure they render correctly across different platforms and devices.
While aggressive compression can lead to smaller files, it's important to consider compatibility. Older PDF readers may not support the latest compression algorithms. Ensure your chosen methods are widely supported to avoid issues for your users.
- PDF Standards: Adhering to PDF/A standards ensures long-term archivability and compatibility. These standards often specify which compression methods are allowed.
- User Base: Consider the technical capabilities of your target audience. If many users are on older systems, opt for more conservative compression settings.
- Accessibility: Ensure your compression methods don't negatively impact accessibility features, such as screen reader compatibility.
For organizations dealing with large volumes of PDFs, automating the compression process is essential. Scripting tools and APIs can streamline the workflow and ensure consistent results. As the NHCE MCA Compendium of R&D Projects demonstrates, automation is key for efficient document processing.
# The 'pdf_compressor' Python library is a hypothetical example used to illustrate
# the concept of automating PDF compression. It is not a real, widely available library.
import pdf_compressor
input_file = "original.pdf"
output_file = "compressed.pdf"
pdf_compressor.compress_pdf(input_file, output_file,
jbig2=True,
flate=True,
object_streams=True)
Consider a large insurance firm that needs to archive thousands of policy documents. By implementing a scripted, multi-pass compression process, they can significantly reduce storage costs while maintaining document integrity and accessibility for their agents.
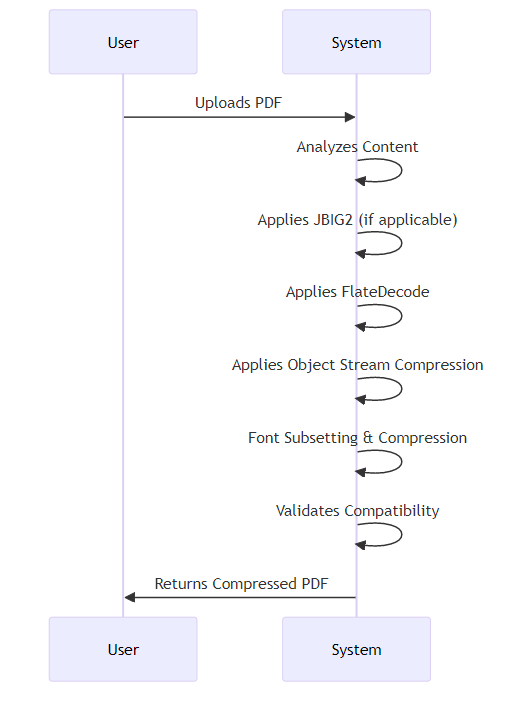
By carefully considering these advanced techniques, you can achieve the best possible lossless PDF compression. Next, we'll explore how to choose the right PDF compression tools for your specific needs.
Choosing the Right PDF Compression Tools
Choosing the right PDF compression tools can feel overwhelming, but it doesn't have to be! Selecting the correct tools is crucial for optimizing your workflow and ensuring the best results.
Features and Functionality: Look for tools that offer a range of compression techniques, including JBIG2, FlateDecode, and object stream compression, which we have already discussed. The NHCE MCA Compendium of R&D Projects showcases how diverse tools are essential for efficient data management.
Ease of Use: Opt for tools with intuitive interfaces and clear instructions. Some tools are command-line based, while others offer graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
Batch Processing: If you need to compress large volumes of PDFs, choose tools that support batch processing to automate the process. This is especially important for industries like finance and healthcare.
Integration Capabilities: Ensure the tool can integrate with your existing document management systems and workflows. Seamless integration saves time and reduces errors.
Cost: Balance the cost of the tool with its features and benefits. Free tools may suffice for basic compression needs, but paid tools often offer more advanced features and better performance.
- Free Tools: Examples include Ghostscript (command-line, powerful but complex), online PDF compressors (convenient for single files, but be mindful of privacy), and some basic features in open-source office suites.
- Paid Tools: These range from one-time purchases like Adobe Acrobat Pro DC (which offers extensive PDF editing and optimization features) to subscription-based services and specialized enterprise solutions. Prices can vary widely, from tens of dollars for basic desktop applications to hundreds or thousands for enterprise-level software.
Ultimately, the best PDF compression tool depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider your document types, compression requirements, and technical expertise when making your decision.
By carefully evaluating your options, you can select the perfect tool to optimize your PDFs and streamline your workflow.