Mastering File Format Conversion: A Comprehensive Guide for Professionals and Students
Why File Format Conversion Matters
Did you know that over 3 billion files have been converted using online tools? File format conversion is a fundamental process that ensures data remains accessible, usable, and optimized across various platforms and applications.
Different software and systems often require specific file formats. Without conversion, accessing or editing a file on a different platform can be impossible. Conversion ensures compatibility, allowing seamless data exchange between different systems. For example, a hospital using a proprietary image format might need to convert patient scans to a more universal format like DICOM for sharing with other specialists. Choosing the right format also avoids vendor lock-in, giving you more control over your data. Vendor lock-in happens when you're tied to a specific software or platform because your data is in a format only that system can read. By converting to more universal or open formats, you can easily move your data to different, potentially cheaper or more flexible, solutions without being stuck with a single provider that might raise prices or discontinue support.
Older file formats can become obsolete over time, making it difficult to access important data. By converting these files to modern, open standards, you ensure long-term data preservation. This is especially crucial for digital archiving, where historical records need to remain accessible for decades. Think of a library needing to convert old word processor documents into a PDF/A format to preserve them.
Different file formats are optimized for different purposes. For instance, a high-resolution image might be ideal for print but too large for a website. Conversion allows you to tailor files for specific applications, reducing file size and improving performance. Consider a marketing team converting large video files to smaller, web-friendly formats for social media campaigns. Convertio supports conversion between 300+ formats.
By understanding why file format conversion matters, you can take steps to ensure your data remains accessible, usable, and optimized for any situation. The next section will explore the different types of file formats and their common use cases.
Common File Format Conversion Types
Did you know that file format conversion isn't just about compatibility, it's about unlocking the potential of your data? Let's dive into some common types of file format conversion and how they impact various industries.
One of the most frequent conversion needs is between document formats. Converting a PDF (Portable Document Format) to an editable DOCX (Microsoft Word Open XML Document) allows users to modify content. Similarly, converting a TXT (plain text) file to DOCX or PDF enhances formatting and presentation.
- PDF to DOCX: Ideal for editing contracts, reports, or any document where changes are required.
- TXT to DOCX/PDF: Useful for creating professional-looking documents from simple text files.
- Considerations: Maintaining original formatting, properly handling embedded images, and using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) to convert scanned documents into editable text are crucial. OCR is a technology that allows computers to "read" text from images, like scanned documents or photos, and convert it into actual editable text. This is super important for making scanned documents searchable and editable. For formatting and images, complex layouts can be tricky, and sometimes you need specialized tools to get it just right.
Image conversion is essential for optimizing visuals for different platforms and purposes. This includes converting between raster formats (like JPG and PNG) and vector formats (like SVG).
- Raster to Vector: Converting a photograph (raster) to a scalable graphic (vector) for logos or illustrations.
- Web vs. Print: Optimizing images for web use often involves converting to JPG or WEBP for smaller file sizes. For print, TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) ensures high resolution.
- Considerations: Weighing lossy (JPG) versus lossless (PNG) compression, maintaining image quality, and preserving transparency (PNG) are key factors. Lossy compression, like in JPGs, makes files smaller by discarding some data, which can slightly reduce quality. Lossless compression, like in PNGs, keeps all the original data, so quality is perfect, but the files are usually bigger.
Audio and video conversion addresses compatibility issues across devices and platforms. It also helps in reducing file sizes for easier sharing and streaming.
- Audio Codecs: Converting between MP3, WAV, and other audio codecs ensures compatibility with different music players and devices.
- Video Formats: Converting video files to MP4 ensures they play correctly on various devices and platforms.
- Considerations: Balancing bitrate, resolution, frame rate, and overall audio/video quality is important to achieve the desired result. Bitrate affects audio quality and file size (higher bitrate usually means better quality and bigger files). Resolution determines the detail in video (higher resolution means sharper images and bigger files). Frame rate is how many images per second are shown, affecting how smooth the video looks (higher frame rate means smoother motion and bigger files).
Understanding these common file format conversion types is essential for anyone working with digital data. Next, we'll explore how to choose the right conversion tools for your specific needs.
Tools and Technologies for File Format Conversion
Choosing the right tools and technologies is crucial for efficient file format conversion. Did you know that the right tool can cut conversion time by up to 50%? Let's explore some of the options available.
Online file converters are a convenient option for users who need to perform occasional conversions or work with smaller files. These tools operate in the cloud, eliminating the need to download and install software.
- Convenient for one-off conversions and small files. These platforms are easily accessible through a web browser, making them ideal for quick conversions on any device. For example, a student might use an online converter to quickly change a document from PDF to DOCX for editing.
- Examples: Convertio, FreeConvert.com, ConvertFiles. These are popular choices due to their ease of use and support for a wide range of file formats.
- Considerations: File size limits, security, and privacy. Users should be mindful of the file size limitations imposed by these services. It's also important to review the platform's privacy policy to understand how your files are handled and secured.
Desktop software offers more advanced features and greater control over the conversion process. These applications are installed directly on your computer, providing enhanced functionality and security.
- Offers more features and control over conversion settings. Desktop software often includes options for batch conversion, detailed customization of output settings, and offline access. Professionals in fields like graphic design or video editing might prefer desktop software for its precision and control.
- Suitable for batch conversions and large files. Desktop applications are well-suited for converting multiple files simultaneously or handling large files that may exceed the size limits of online converters.
- Examples: Adobe Acrobat, Microsoft Office, specialized conversion software. These tools provide a comprehensive suite of features for managing and converting various file types.
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs and priorities. Whether you opt for the convenience of online converters or the power of desktop software, understanding the available options will help you make an informed decision. In the next section, we'll examine document management solutions.
Leveraging APIs for Automated Conversion
Did you know that integrating apis for file conversion can automate processes, saving businesses countless hours? Conversion apis offer a programmatic way to access file format conversion services, making them ideal for integration into various applications and workflows.
Conversion apis provide programmatic access to file conversion services. This allows developers to embed conversion functionality directly into their applications. Instead of relying on manual uploads and downloads, apis enable automated, server-to-server file processing.
They are suitable for high-volume conversions and automated workflows. For instance, an e-learning platform might use an api to automatically convert uploaded documents into a consistent format for students. This eliminates manual intervention and ensures seamless integration with the platform's content management system.
Examples of conversion apis include the CloudConvert api, Zamzar api, and FreeConvert api. These apis support a wide range of file formats and conversion options, providing developers with the flexibility to meet diverse conversion needs. Many specific apis are available from various providers.
Conversion apis are particularly useful in document management systems, content management systems, and e-commerce platforms. A law firm could use an api to automatically convert client documents into a secure, searchable pdf format upon upload. This streamlines document management and ensures compliance with industry standards.
They facilitate automated pdf generation, image processing, and audio/video transcoding. A digital marketing agency might use an api to automatically generate optimized image formats for different social media platforms. This ensures consistent branding and improved performance across channels.
Conversion apis also allow for integrating conversion capabilities into mobile apps and web services. Imagine a real estate app that lets users upload property photos, which are then automatically converted to a standard format for display. This enhances user experience and simplifies content management.
The following code example illustrates a basic api call using Python. Keep in mind that this example is conceptual as it does not use a real api key, as that would be a security violation.
import requests
API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY"
URL = "https://api.example-converter.com/convert"
def convert_file(input_file, output_format):
with open(input_file, 'rb') as f:
files = {'file': f}
data = {'output_format': output_format, 'api_key': API_KEY}
response = requests.post(URL, files=files, data=data)
if response.status_code == 200:
# A successful response might contain a URL to the converted file,
# or the file content directly, depending on the API.
# For this example, we'll assume it returns the file content.
with open(f'converted_file.{output_format}', 'wb') as outfile:
outfile.write(response.content)
print("File converted successfully!")
else:
# Common error responses might include status codes like 400 (Bad Request)
# or 401 (Unauthorized), along with an error message.
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}, {response.text}")
convert_file('document.docx', 'pdf')
This example demonstrates how to upload a file, specify the target format, and download the converted file. Handling errors and managing authentication are crucial aspects of api integration.
Understanding how to leverage apis for automated conversion is essential for streamlining document workflows and enhancing application functionality. In the next section, we'll explore the future of file format conversion.
Best Practices for File Format Conversion
File format conversion can be tricky, but with the right strategies, you can ensure a smooth and accurate process. Let's explore some best practices to keep in mind.
Consider the intended use of the file and the capabilities of the target software. For example, if you need to edit a document, converting a PDF to DOCX makes sense. However, if you want to archive a document, PDF/A is a better choice.
Balance file size, quality, and compatibility. Image conversion often involves trade-offs. JPG offers smaller file sizes but can sacrifice quality, while PNG preserves quality but results in larger files. Consider your specific need to determine the best balance.
Research the best format for archiving and long-term preservation. Certain formats, like TIFF for images and PDF/A for documents, are designed to ensure long-term accessibility and prevent obsolescence.
Be aware of potential data loss during conversion, especially with lossy compression methods like JPG. Whenever possible, use lossless formats like PNG or TIFF to avoid quality degradation.
Verify the converted file to ensure accuracy and completeness. Open the converted file and check for any errors, missing data, or formatting issues. This step is crucial, especially when dealing with important documents or images.
Use appropriate settings to minimize data loss. Many conversion tools offer options to adjust quality, resolution, and other parameters. Experiment with these settings to find the optimal balance between file size and data integrity. For example, when using the
bfconvertcommand line tool, a command-line utility often used in scientific imaging, image quality can be specified. According to Bio-Formats documentation, quality must take a value between0.25and1.0when using-compression JPEG.Be cautious when using online converters with sensitive data. As previously discussed, online converters can be convenient, but they also pose security risks. FreeConvert.com states that they use "256-bit SSL encryption when transferring files and automatically delete them after a few hours."
Choose reputable providers with strong security measures. Look for converters that use encryption, have clear privacy policies, and are transparent about how they handle your data.
Consider using desktop software or APIs with secure data transfer protocols. As noted earlier, desktop software and apis offer more control over security.
By following these best practices, you can confidently convert files while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency. The next section will discuss file conversion in document workflows.
File Conversion in Document Workflows
Did you know that integrating file conversion into your document workflows can save hours of manual work? By automating these processes, you ensure consistency and efficiency across your organization.
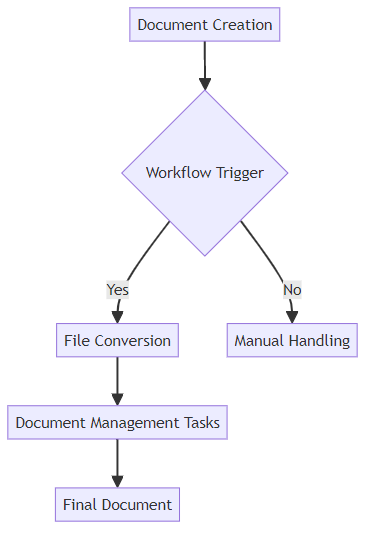
- Automating file conversion as part of a larger document workflow streamlines operations. Instead of manually converting files, set up systems that automatically convert documents when certain actions occur.
- For example, a marketing team could automate the conversion of design files to web-friendly formats as soon as they are approved. This ensures that all online assets are consistently optimized.
- Integrating conversion with other document management tasks like merging, splitting, and signing enhances productivity. Combining these tasks reduces the number of steps required in a workflow.
- Consider a legal firm that automatically converts, merges, and signs documents as part of their contract management. This integration saves time and reduces the risk of errors.
- Ultimately, the goal is to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort. Automation minimizes the need for human intervention, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
Converting documents to accessible formats, such as tagged PDFs, is essential for users with disabilities. Tagged PDFs provide structural information that screen readers can use to navigate the document effectively.
Educational institutions can convert course materials into tagged PDFs to ensure all students have equal access. This commitment enhances inclusivity and meets accessibility standards.
Using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) makes scanned documents searchable and accessible. OCR converts images of text into actual text, allowing screen readers and search engines to index the content.
Libraries and archives can use OCR to digitize historical documents, making them available to a wider audience. This not only preserves the documents but also increases their usability.
Following accessibility guidelines and standards ensures compliance and promotes inclusivity. Adhering to standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) helps create documents that are usable by everyone.
Using consistent file formats facilitates seamless collaboration among team members. When everyone works with the same file types, compatibility issues are minimized.
For instance, a construction company could mandate using a standard CAD format for all project blueprints. This ensures that architects, engineers, and contractors can easily exchange and view the files.
Converting files to a common format before sharing simplifies the review process. This ensures that recipients can open and view the document without needing specific software.
A financial firm might convert reports to PDF before sending them to clients, ensuring they can be viewed on any device. This simplifies communication and enhances the client experience.
Maintaining version control helps track changes and avoid compatibility issues. Using a document management system that supports versioning ensures everyone is working with the latest version of a file.
By integrating file conversion into your document workflows, you can significantly improve efficiency, accessibility, and collaboration. Next, we'll explore the future of file format conversion.
The Future of File Format Conversion
The future of file format conversion is looking pretty dynamic, driven by a few big trends: ai, cloud computing, and the push for open standards.
ai is going to play a huge role. Think about intelligent format detection – ai systems that can figure out what kind of file you have even if it's mislabeled or in an obscure format. Then there's automated quality assessment. Instead of manually checking if a conversion went well, ai could analyze the output for errors or degradation. This means more accurate conversions with less human oversight. We might even see ai that can predict the best conversion settings for a specific file type to maintain maximum quality while minimizing size.
Cloud-based conversion services are already big, and they're only going to get bigger. The cloud offers incredible scalability, meaning you can convert massive amounts of files without worrying about your own hardware limitations. It also means accessibility – you can convert files from anywhere with an internet connection. This is perfect for remote teams or individuals who don't have powerful computers. Imagine a global company needing to convert thousands of documents daily; the cloud makes that feasible and cost-effective.
And then there are emerging open standards. As more industries adopt open formats, the need for conversion might decrease in some areas, but it will also increase the demand for converting to these open standards. This promotes interoperability – the ability for different systems to work together seamlessly. For example, if a new open standard for medical imaging emerges, there will be a surge in demand to convert existing proprietary formats into this new standard, making data sharing much easier and less dependent on specific vendors. This could lead to more diverse file formats being supported, but also a greater need for robust conversion tools to bridge the gaps.
Potential future use cases could include real-time conversion during video calls to ensure everyone sees content in their preferred format, or automated conversion of research papers into standardized formats for easier cross-referencing and analysis. The possibilities are pretty exciting.