Metadata Injection and Standardization: Streamlining PDF Processing for Professionals
Understanding Metadata: The Foundation of Document Intelligence
Metadata is often described as "data about data," but what does that really entail? Think of it as the DNA of a document, carrying vital information that unlocks its full potential. This hidden layer is the key to unlocking document intelligence, enabling streamlined workflows and enhanced accessibility.
- Definition: Metadata provides context for any document. It's the who, what, when, where, and how that adds clarity to raw information. For instance, a healthcare provider can quickly locate a patient's medical history using metadata tags like patient ID, date of birth, and treatment codes.
- Identification: Metadata ensures proper document identification. A retail company can categorize invoices by vendor, date, and product type, facilitating efficient tracking of expenses and inventory.
- Organization: Metadata is crucial for organization. A finance firm can retrieve specific client contracts using metadata fields such as client name, contract type, and effective dates.
- Retrieval: Metadata makes document retrieval easier.
PDF metadata specifically includes a range of fields that provide essential details about the document. Common fields include:
- Title, Author, Subject
- Keywords
- Creation and Modification Dates
- Creator and Producer Applications
- PDF Version
Well-structured metadata isn't just about convenience; it's about inclusivity. It ensures documents are accessible to everyone, including users with disabilities. Metadata also drives automation, enabling systems to process and manage documents with minimal human intervention.
As we move forward, keep in mind that understanding metadata is the first step in leveraging the full power of your documents. In the next section, we'll explore the role of metadata in PDF processing and document management.
Metadata Injection: Adding Value to Your PDFs
Metadata injection is like giving your PDFs a digital boost, ensuring they stand out in the crowded digital landscape. Let's dive into how you can effectively add value to your PDFs through metadata.
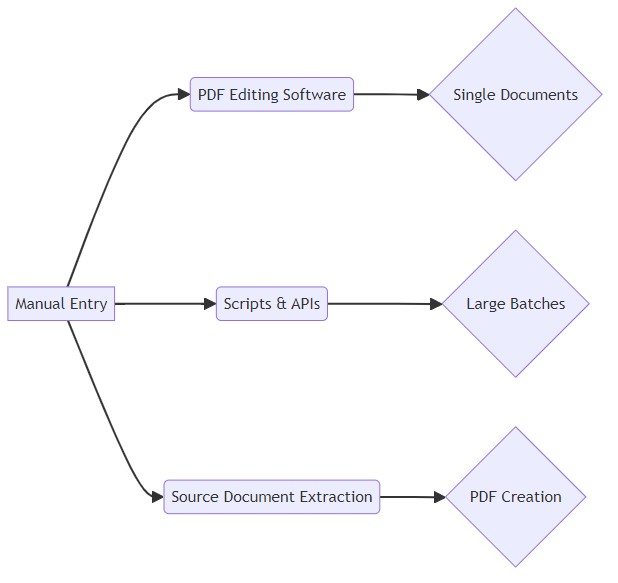
There are several ways to inject metadata into your PDFs, each offering different levels of control and automation:
- Manual metadata entry is the most straightforward method. You can use PDF editing software like Adobe Acrobat Pro or Foxit PhantomPDF to manually add or modify metadata fields. This approach is suitable for single documents or small batches where precision is key.
- Automated metadata injection uses scripts and apis to streamline the process. This method works best for large volumes of documents where consistency and efficiency are essential. For example, a law firm might use a script to automatically add client names, document types, and dates to hundreds of legal filings.
- Metadata extraction from source documents is another efficient technique. During PDF creation, metadata can be automatically extracted from the original document (e.g., a Word file) and embedded into the PDF. This ensures that vital information is carried over seamlessly.
Choosing the right tools is crucial for effective metadata injection. Several software options and libraries offer robust metadata capabilities.
- PDF editing software such as Adobe Acrobat Pro and Foxit PhantomPDF provide a user-friendly interface for manual metadata management. These tools allow users to directly edit metadata fields, add keywords, and ensure compliance with accessibility standards.
- PDF libraries and apis like iText and PDFBox enable programmatic metadata injection. These tools are invaluable for developers who need to automate metadata processes within custom applications or workflows.
- Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs and technical expertise. If you're working with a small number of documents, a PDF editor might suffice. For larger projects requiring automation, PDF libraries and apis are more appropriate.
Effective metadata injection requires attention to detail and adherence to best practices:
- Ensuring accuracy and consistency is paramount. Inaccurate or inconsistent metadata can lead to confusion and errors. Always double-check metadata values and use standardized formats.
- Using controlled vocabularies and taxonomies can improve searchability and organization. By using predefined terms and categories, you ensure that metadata is consistent across all documents.
- Regularly reviewing and updating metadata is essential to maintain its relevance and accuracy. As documents evolve, metadata should be updated to reflect changes in content and context.
With the right methods, tools, and best practices, you can transform your PDFs into valuable assets that enhance document management, accessibility, and workflow automation.
Now that you understand how to inject metadata, let's explore the critical role of standardization in ensuring interoperability and consistency across your documents.
Metadata Standardization: Ensuring Interoperability and Consistency
Metadata standardization is the unsung hero of seamless document workflows, saving countless hours and preventing frustrating data silos. Imagine trying to piece together a global puzzle with pieces from different sets – that's what it's like without standardized metadata.
Why Standardization is Crucial: Metadata standards ensure systems can exchange and interpret data correctly. Without standardization, a healthcare provider's system might misinterpret patient data from another facility, leading to errors in treatment.
Benefits of Established Schemas: Established metadata schemas like the Dublin Core Metadata Element Set provide a common language for describing resources. This allows libraries worldwide to catalog books in a way that is universally understood, making resource sharing and discovery much more efficient.
Compliance with Industry Standards: Industry-specific standards ensure vital data is consistently captured. For example, compliance with financial reporting standards like XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language) ensures that all financial documents include the necessary metadata for auditing and regulatory purposes, allowing for machine-readable financial data.
Dublin Core Metadata Element Set: This is a foundational standard, which provides a basic set of elements to describe a wide range of resources. It includes fields like Title, Creator, Subject, Description, and Date.
ISO 19115 and Geospatial Metadata Standards: These standards cater to geospatial data, ensuring that location-based information is accurately and consistently represented. For example, environmental agencies use these standards to manage and share data related to geographic features, such as rivers, forests, and protected areas.
PDF/A Standards for Archiving: PDF/A standards are designed for the long-term preservation of electronic documents. These standards mandate that all necessary information for rendering the document is embedded within the file itself, ensuring it remains accessible and visually consistent for years to come. For PDF/A compliance, specific metadata elements like the document's title, author, and creation date are crucial and must be embedded in a standardized way to guarantee long-term accessibility and prevent future rendering issues.
Roemmich, D., et al. (2022) highlight the importance of the Global Ocean Ship-based Hydrographic Investigations Program (GO-SHIP) and the Argo Program in providing sustained subsurface ocean observations. These programs exemplify robust metadata practices by meticulously documenting the collection, processing, and quality control of vast amounts of oceanographic data, ensuring its long-term usability and interoperability for researchers worldwide. This mirrors the principles of metadata standardization needed for any large-scale data management effort, including PDF document management.
- Selecting the Right Standard: Choose a standard that aligns with your organization's needs and industry requirements. A small design firm might find Dublin Core sufficient, while a large engineering firm might need more specialized standards like ISO 19115 for geospatial data.
- Developing a Metadata Policy: A metadata policy outlines how metadata should be created, managed, and updated. This ensures consistency across all documents and data assets.
- Training Staff: Provide training on metadata best practices to ensure everyone understands how to create and maintain high-quality metadata.

Now that we've covered metadata standardization, let's explore how these principles translate into practical applications for enhancing document workflows.
Practical Applications: Enhancing Document Workflows with Metadata
Metadata isn't just for archival purposes; it's a dynamic tool that can revolutionize how professionals manage their daily document workflows. By embedding metadata strategically, you can unlock powerful automations and efficiencies that save time and reduce errors.
Creating advanced search filters becomes straightforward with metadata. Instead of sifting through countless documents, a human resources department can quickly locate employee records by filtering on metadata such as department, job title, or performance review date.
Implementing faceted search provides an intuitive way to discover documents. For example, a construction company can use faceted search to narrow down project documents by location, architect, contractor, or permit type, making it easy to find exactly what they need.
Leveraging metadata for full-text search optimization ensures that even the most detailed queries return relevant results. A research institution can use metadata to index research papers by author, keywords, and publication date, improving the accuracy and speed of search results.
Using metadata to trigger automated workflows streamlines document handling. An insurance company can automatically route claims to the appropriate adjuster based on metadata fields like claim type, amount, and geographic location.
Implementing rule-based routing based on metadata values ensures documents reach the right people. For instance, in a manufacturing plant, safety incident reports can be routed to the safety manager, plant supervisor, and HR department based on incident severity and affected area.
Integrating metadata with document approval systems simplifies the approval process. A legal firm can use metadata to automatically notify senior partners when a junior associate submits a contract for review, accelerating turnaround times.
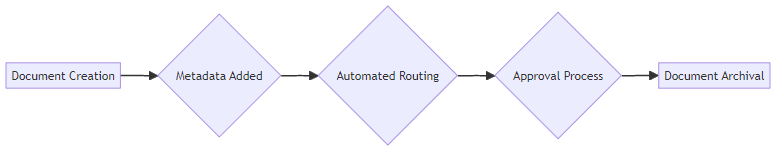
- Controlling access to sensitive documents becomes more precise with metadata. A government agency can restrict access to classified documents based on security clearance levels specified in the metadata.
- Implementing metadata-driven retention policies ensures compliance with regulatory requirements. A financial institution can automatically archive or delete client records based on retention schedules defined by metadata fields like account type and creation date.
- Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA is simplified with metadata. An e-commerce business can use metadata to track customer consent preferences and automatically redact personal data when a customer requests it.
These practical applications demonstrate how metadata can transform document workflows from manual, error-prone processes to automated, efficient systems. By integrating metadata into your document strategy, you can improve searchability, automate routing, and enhance security.
In the next section, we'll examine specific metadata standards relevant to PDF documents.
PDF Processing with Metadata
Metadata is the unsung hero of PDF efficiency, but what happens when the very tools meant to enhance it inadvertently compromise its integrity? Let’s explore how to navigate the complexities of PDF processing while safeguarding metadata.
When you create a PDF, the software you use plays a key role in how metadata is handled.
- Embedding metadata during PDF creation from sources like Word documents or images can streamline workflows. Many applications automatically transfer titles, authors, and keywords.
- PDF creation tools supporting metadata standards are essential for interoperability. These tools ensure compliance with standards like Dublin Core, enabling seamless data exchange between systems. For example, Adobe Acrobat Pro and some open-source libraries like PDFBox can embed metadata according to specified standards.
- Automating metadata population during PDF generation is efficient for large-scale operations. For instance, a university can automatically add student names, course titles, and assignment details to PDFs using scripts, perhaps by reading from a database or spreadsheet.
Converting files to PDF format is a common task, but it can also be a source of metadata loss.
- Ensuring metadata is preserved during file format conversion requires careful selection of conversion tools. Some services strip metadata by default, so look for options that explicitly support metadata retention.
- Selecting document conversion services that support metadata mapping can streamline complex conversions. Metadata mapping allows you to transfer specific fields from one format to corresponding PDF fields.
- Validating metadata after conversion is a crucial step to ensure accuracy. A simple spot-check can prevent errors and maintain data integrity.
Sometimes, PDFs get corrupted, and metadata is often one of the first casualties.
- PDF repair tools can sometimes alter or remove metadata in the process of fixing file errors. Always back up your PDFs before attempting repairs.
- Strategies for recovering lost or corrupted metadata include using specialized software that attempts to salvage data from damaged files. Tools like Stellar Repair for PDF or DataNumen PDF Repair might help. In some cases, you might need to revert to the original source document or use file carving techniques if the file structure is severely damaged.
- Best practices for maintaining metadata integrity during PDF repair include using reliable repair tools and validating metadata immediately after the repair process.
Navigating these aspects of PDF processing ensures that your documents remain intelligent, accessible, and well-managed.
Next, we'll uncover the specific metadata standards that are relevant to PDF documents.
Leveraging PDF7 for Seamless Document Management
Metadata is the backbone of modern document management, but how can you ensure that your document tools are up to the task? Let's explore how to leverage PDF7's features for a more streamlined and secure document workflow.
PDF7 is a hypothetical platform designed to simplify PDF processing, saving time and resources.
PDF7 offers a suite of online tools to simplify PDF processing, saving time and resources.
- Effortlessly convert, compress, and edit PDF files online, eliminating the need for software downloads. This is particularly useful for teams collaborating on documents across different devices and operating systems.
- Convert PDFs to various formats, including Word, Excel, JPG, and PNG, ensuring compatibility with different software applications. This flexibility streamlines workflows when sharing documents with external partners or clients.
- Use translation and summarization tools to enhance document understanding, particularly useful for global teams working with multilingual content. You can quickly grasp the main points of lengthy reports or translate documents for international colleagues.
Security and accessibility are paramount in professional document management, and PDF7 provides features to address both.
- Secure your sensitive information with PDF protection features, preventing unauthorized access and modifications. For example, you can apply password protection to confidential financial reports or legal documents.
- Unlock password-protected PDFs with ease, recovering access to essential files when passwords are forgotten. This saves time and avoids disruptions in document workflows.
- Optimize PDFs for screen readers and accessibility standards, ensuring compliance with regulations and inclusivity for all users. This is crucial for government agencies and educational institutions needing to meet accessibility requirements.
PDF7 offers a range of AI-powered tools that can significantly enhance productivity.
- Utilize the Paraphrasing Tool, Translator, Summarizer, Grammar Checker, Proofreader, Legal Document Drafting Generator, and Text Extender to create better content, enhancing communication and efficiency. These tools are particularly beneficial for content creators, marketers, and legal professionals.
- Create professional legal documents with the AI-powered drafting generator, saving time and resources on routine legal tasks. Small law firms and solo practitioners can leverage this feature to increase efficiency.
- Improve your writing and refine your text with our intelligent tools, ensuring clarity and accuracy in all your documents. This is valuable for anyone who needs to produce high-quality written content, such as grant writers, journalists, and academic researchers.
By integrating PDF7's capabilities into your document management strategy, you can enhance efficiency, security, and accessibility while leveraging ai to boost productivity. In the next section, we'll wrap up our discussion with a look at the future trends in PDF processing and metadata management.
The Future of Metadata: AI, Automation, and Beyond
The future of metadata is dynamic, propelled by advancements in ai and automation. How can these innovations reshape document workflows and unlock new levels of efficiency?
Ai and machine learning automate metadata extraction, which saves time and reduces manual errors. Imagine ai algorithms scanning invoices to automatically identify vendor names, dates, and amounts. For example, an ai could process a batch of scanned invoices, extract key fields like invoice number, total amount, and due date, and automatically populate these into a structured database.
Semantic information enrichment improves metadata quality. For example, an ai system might add related concepts or synonyms to keywords, making documents easier to find. If a research paper is tagged with "climate change," an ai could enrich this by adding related terms like "global warming," "greenhouse gases," or "carbon emissions," creating a richer search experience.
Ai algorithms improve metadata consistency across large document sets. This helps to avoid discrepancies and ensures data integrity. For instance, an ai could be trained to identify and standardize author names, ensuring "John Smith," "J. Smith," and "Smith, John" are all recognized as the same entity.
Automated metadata creation streamlines document processing. Think of a system that automatically assigns metadata based on document content and predefined rules.
Event-triggered workflows improve efficiency. For instance, when a document is created, a workflow could automatically populate metadata fields based on user inputs.
Integration with business systems enhances data flow. For example, metadata from a crm could automatically populate fields in related contracts.
The convergence of metadata, ai, and semantic technologies leads to more intelligent document processing. This could allow systems to understand the context and relationships between documents.
The rise of knowledge graphs enables new forms of document analysis. These graphs can visually represent the relationships between different concepts and entities within documents.
Document management evolves from simple repositories to knowledge ecosystems. Systems will provide users with access to information and intelligent tools for analysis and collaboration.
As technology evolves, metadata will become even more integrated with ai and automation, driving new levels of document intelligence.